Glaucoma
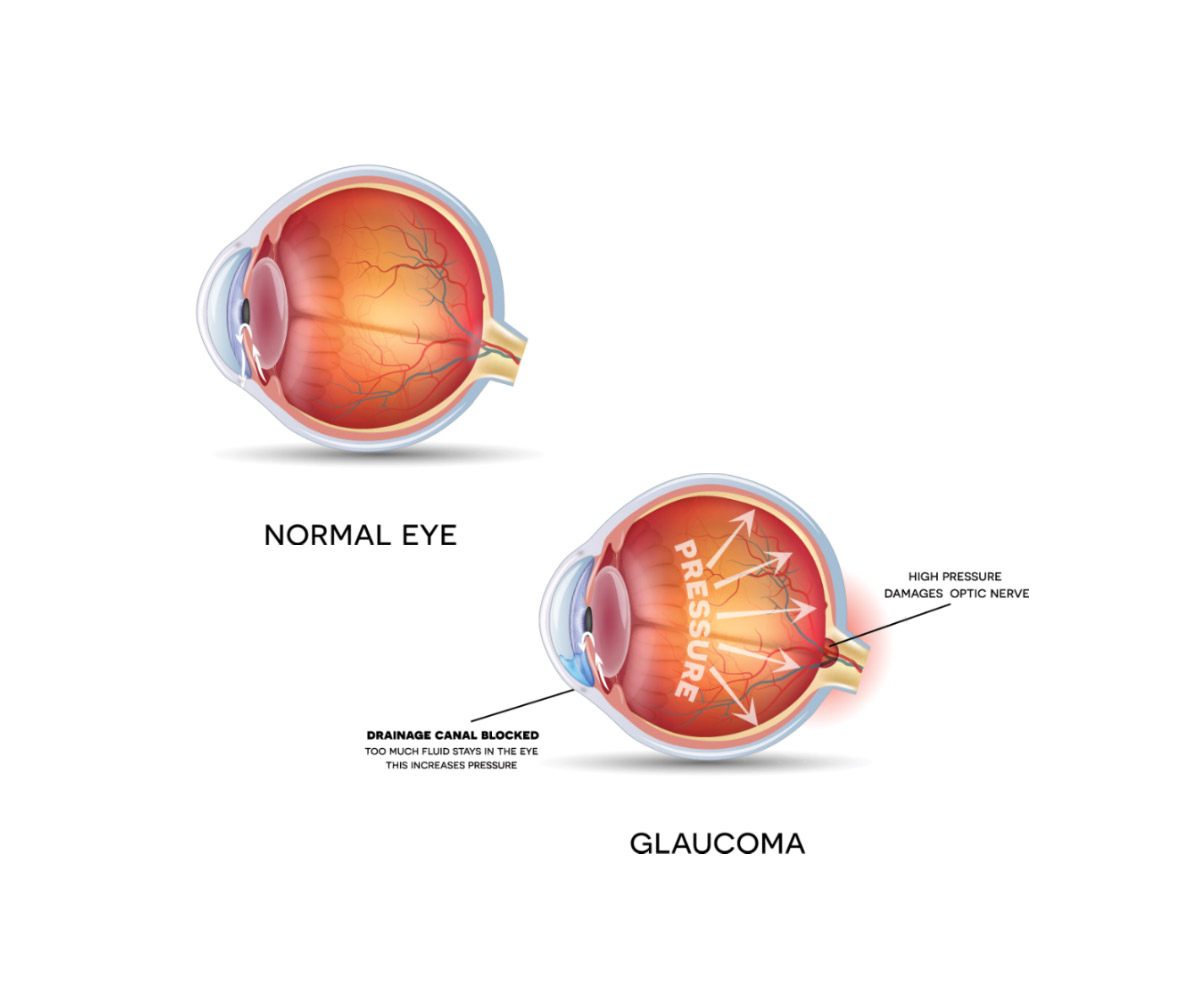
Glaucoma is a common eye condition where the optic nerve, which connects the eye to the brain, becomes damaged.
It’s usually caused by fluid building up in the front part of the eye, which increases pressure inside the eye. Glaucoma can lead to loss of vision if it’s not diagnosed and treated early. It can affect people of all ages, but is most common in adults over the age of 60years.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Glaucoma does not usually cause any symptoms to begin with. It tends to develop slowly over many years and affects the edges of your vision (peripheral vision) first. For this reason, many people do not realise they have glaucoma, and it’s often only picked up during a routine eye test.
If you do notice any symptoms, they might include blurred vision, or seeing rainbow-coloured circles around bright lights. Both eyes are usually affected, although it may be worse in one eye.
If you think you may have glaucoma go to you Optometrist. Early diagnosis and treatment can help stop your vision getting worse.

Treatments for glaucoma
It’s not possible to reverse any loss of vision that occurred before glaucoma was diagnosed, but treatment can help stop your vision getting worse. The treatment recommended for you will depend on the type of glaucoma you have, but the options are:
- eyedrops – to reduce the pressure in your eyes
- laser treatment – to open up the blocked drainage tubes or reduce the production of fluid in your eyes
- surgery – to improve the drainage of fluid.
Useful Links
